You may wonder why I have chosen to include eating as a word associated with Cognitive Behavioural Therapy. Well the connection between thoughts, beliefs, emotions and behaviours is never more clear than when we explore our eating habits.
Remember that CBT is all about becoming more aware of the effect our thoughts and beliefs have on our behaviours and emotions. In today’s modern world we are awash with opportunities to eat more and think less. We w ander around the shops in our local towns on a Saturday, passing increasing numbers of bakers, chip shops, burger bars, fast food shops, cafes, restaurants … the choice is seemingly limitless. We go home and sit in front of our television screen where we are shown advertisement after advertisement encouraging us to try this new food or that one. It is not surprising that we find ourselves giving in to temptation and eating something we hadn’t planned to, didn’t need to, and often didn’t really want to eat!
ander around the shops in our local towns on a Saturday, passing increasing numbers of bakers, chip shops, burger bars, fast food shops, cafes, restaurants … the choice is seemingly limitless. We go home and sit in front of our television screen where we are shown advertisement after advertisement encouraging us to try this new food or that one. It is not surprising that we find ourselves giving in to temptation and eating something we hadn’t planned to, didn’t need to, and often didn’t really want to eat! 
So how can we reverse the trend and eat less and think more about what we are eating?
- Cultivate a connection between your mind and your body. Listening to your body means that you will be more aware of when you are actually hungry. This will encourage you to stop impulse eating when you are not genuinely hungry.
- Eat for energy not for entertainment. Don’t eat through boredom, find something interesting to occupy your attention instead.
- Eat because your body needs nutrients, not because your emotions need support. If you are feeling unhappy, eating for “pleasure” only ultimately results in you feeling unhappy and guilty because of your out of control eating habits. Tackling your emotional and behavioural issues will mean that you no longer feel the need to use food as an emotional crutch. (This is where the cognitive behavioural therapy comes in!)
- Cultivate healthy eating habits: Eat smaller meals more regularly so that your digestive system does not get overloaded and you maintain a steady supply of energy to the body and brain.
- Don’t be taken in by the hype. Foods which are promoted as being “time-saving” are either a drain on your finances or a drain on your health, or both. Allocate time in your day to prepare meals yourself. If you prepare them, you know what has gone into them, and probably more importantly, you know what has been left out.
- Be aware of the physiological connection that our body/mind has with sugar, fat and simple carbohydrates such as white flour: The more we eat these types of foods, the more we set up pathways in the brain which then create cravings for more, thus creating a vicious circle in our subconscious.
- Remember all the benefits of healthy eating: Healthier bodies and healthier minds. We weren’t developed to eat chemical additives, and healthier eating patterns result in better weight management, increased self-confidence and self-esteem as a result of looking better, feeling better and knowing that you control your eating, not the other way round.
- You will notice that as you begin to eat more healthily, your body/mind will gradually wean itself off the cravings for unhealthy foods and your subconscious will begin to “ask” for, and enjoy, more healthy foods.
Next time y ou are about to go in the bakers/chip shop or wherever, try this experiment in food awareness: Stop and ask yourself why you are going in. Are you genuinely hungry? Does your body need that sort of food? Could you be kinder to your body and give it something it really needs, rather than something you feel you want?
ou are about to go in the bakers/chip shop or wherever, try this experiment in food awareness: Stop and ask yourself why you are going in. Are you genuinely hungry? Does your body need that sort of food? Could you be kinder to your body and give it something it really needs, rather than something you feel you want?

 ain—a change of more than 5% of body weight in a month.
ain—a change of more than 5% of body weight in a month. e or embarrassment associated with suffering from depression. Depression, like asthma or a broken leg, is a medical condition, and like any medical condition it responds much better to prompt diagnosis and treatment. If you suspect that either your or somebody you know may be suffering from low mood or depression, a visit to your doctor is always a good idea.
e or embarrassment associated with suffering from depression. Depression, like asthma or a broken leg, is a medical condition, and like any medical condition it responds much better to prompt diagnosis and treatment. If you suspect that either your or somebody you know may be suffering from low mood or depression, a visit to your doctor is always a good idea. 


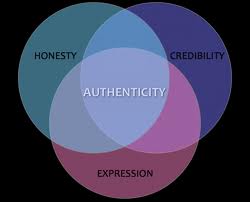 our to live your life according to these and other similar principles, then you are living your life authentically. Living authentically means having an inner integrity and being honest and up-front with yourself, in order that you can be the same with others; being self-aware and understanding what you believe, want and feel. Living your life authentically means that you assess a situation before involving yourself, you sometimes put yourself first, and you only say what you really, honestly, truthfully mean.
our to live your life according to these and other similar principles, then you are living your life authentically. Living authentically means having an inner integrity and being honest and up-front with yourself, in order that you can be the same with others; being self-aware and understanding what you believe, want and feel. Living your life authentically means that you assess a situation before involving yourself, you sometimes put yourself first, and you only say what you really, honestly, truthfully mean.  rson you have become expected to be. When you live your life authentically, you become easier and less stressed to live with, happier to live with and kinder to live with. Authentic living is a win/win situation. So why not free all those thoughts and feelings around expectations of others and allow yourself to develop an inner wisdom in order to live your life through your inner self in a way that feels comfortable and right for you?
rson you have become expected to be. When you live your life authentically, you become easier and less stressed to live with, happier to live with and kinder to live with. Authentic living is a win/win situation. So why not free all those thoughts and feelings around expectations of others and allow yourself to develop an inner wisdom in order to live your life through your inner self in a way that feels comfortable and right for you?